Sunburn vs. Tan: What's the Difference and How to Protect Yourself
Tanning and sunburn are two different skin responses to exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. While both involve reactions to sunlight, they lead to very different results. In this article, we will explore the science behind tanning and sunburn.

Tanning and sunburn are two different skin responses to exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. While both involve reactions to sunlight, they lead to very different results. In this article, we will explore the science behind tanning and sunburn.
What is tanning?
Tanning is the process by which a skin pigment, known as melanin, is produced in response to UV radiation. When the skin is exposed to UVB rays, specialized cells called melanocytes within the epidermis of the skin begin to produce melanin. Melanin is a dark pigment that acts as a natural defense mechanism against harmful UV rays by absorbing and scattering UV rays before they damage the DNA of skin cells.

What is sunburn?
On the other hand, sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive amounts of UV radiation, mainly UVB rays. Unlike tanning, which is a protective mechanism, sunburn is a sign of skin cell damage. When the skin is exposed to UV radiation, the DNA in the skin cells is damaged, triggering an inflammatory response.
The redness, pain, and peeling associated with sunburn are the result of increased blood flow to the affected area as the body attempts to repair the damage. Severe or repeated sunburns can cause long-term skin damage, aging and an increased risk of skin cancer.
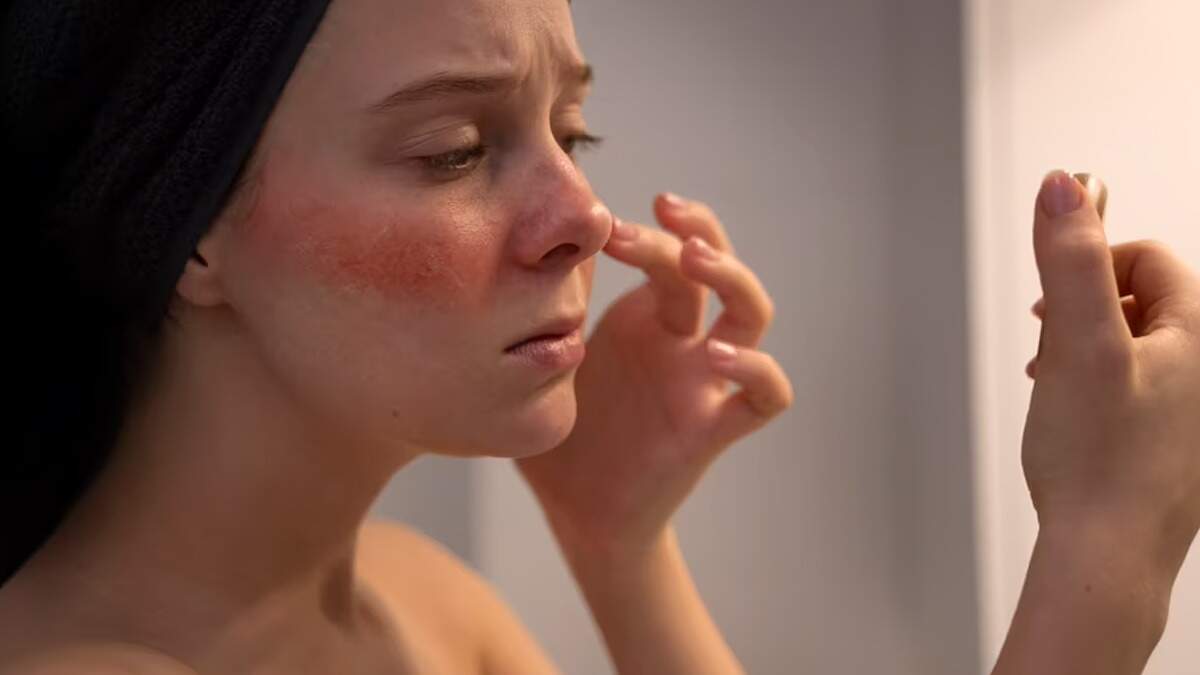
How are tanning and sunburn different?
Here are the main differences between tan and sunburn to help you understand better:
Purpose: Tanning is a natural defense mechanism to protect the skin from UV damage. On the other hand, sunburn is a sign of UV-induced damage to skin cells.
Melanin production: Tanning involves the production of melanin, which darkens the skin to provide protection against UV radiation. A sunburn does not increase melanin production; Instead, it results from damaged skin cells.
Skin reaction: Tanning leads to gradual darkening of the skin, which may provide some level of protection against further UV exposure. Sunburn causes redness, pain and peeling, indicating immediate skin damage.
Time of Exposure: Tanning is caused by prolonged and moderate exposure to the sun's UV rays. Sunburn occurs with acute and excessive exposure, often during peak hours when the sun's rays are at their highest.
