Revamping Critical Care: A Look at India's New ICU Admission & Discharge Guidelines

The Union Health Ministry has issued guidelines for hospitals regarding Intensive Care Unit (ICU) admissions. The guidelines include information on who should be admitted, who should not, the discharge process and minimum supervision requirements while the patient is waiting for a bed. The guidelines have been developed by 24 doctors from different parts of India, including doctors from Canada and Dubai.
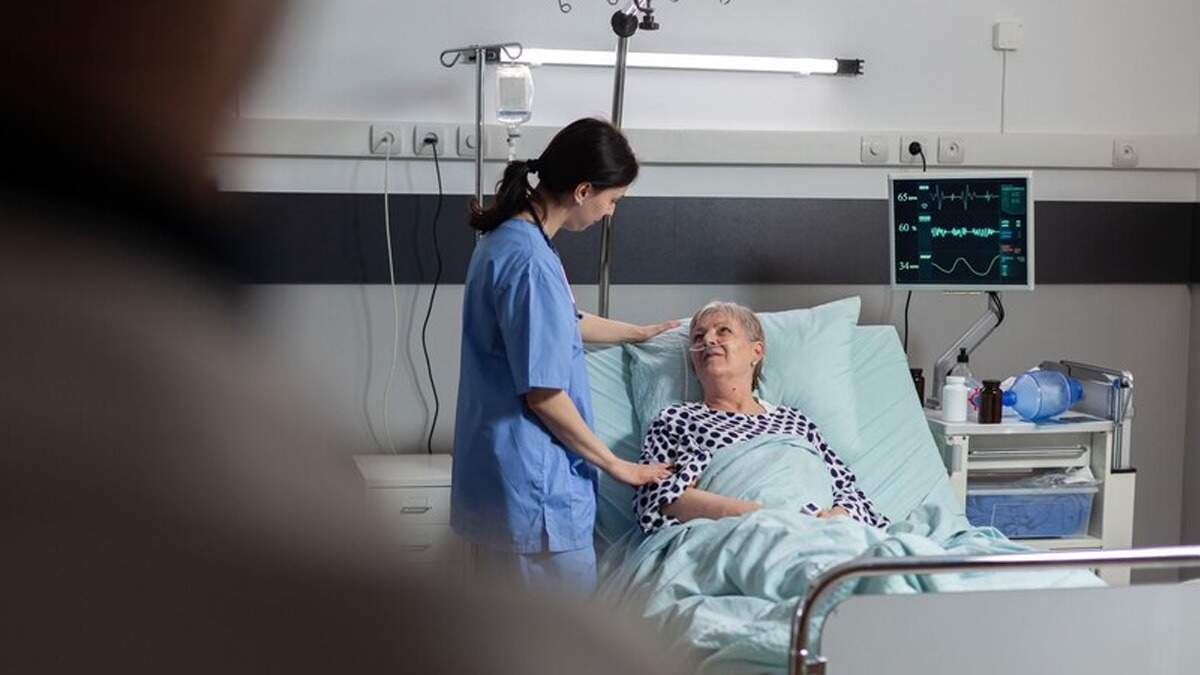

ICU admission criteria
- If someone from your family needs to be admitted to ICU then you should know the following criteria. It is important to know this criteria in advance rather than getting confused especially at the hospital where the whole process of filling the form and everything starts. This may cause a delay in your loved one's treatment.
- The guidelines state that the need to admit a patient to the ICU should be based on organ failure and the need for organ support or the expectation of worsening medical conditions.
- Recent onset of hemodynamic instability Altered level of consciousness (eg, clinical signs of shock, arrhythmia)
- Requirement of respiratory support (eg increased oxygen requirement, de-novo respiratory failure requiring non-invasive ventilation, invasive mechanical ventilation, etc.)
- Patients with severe acute (or acute-on-chronic) illness requiring intensive monitoring and/or organ support Any medical condition or disease with an expectation of deterioration
- Patients who have experienced any major intraoperative complication (eg cardiovascular or respiratory instability)
- Patients who have undergone major surgery, (eg thoracic, thoraco-abdominal, upper abdominal operations, trauma that requires intensive monitoring or are at high risk of developing postoperative complications).
- The guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health also mention who should not be admitted to the ICU. Below is a list of instructions placed in the manual.
Who should not be admitted to ICU?
Guidelines provided by the Ministry of Health stated criteria for critically ill patients who should not be admitted to the ICU. Following are the points listed in the guidelines.
- Patient or next of kin reported refusing admission to ICU
- Any disease with a treatment limitation plan
- Advanced directive against anyone with a living will or ICU care
- Critically ill patients with medical judgment of futility
- A low priority measure in an epidemic or disaster situation where resources are limited (eg beds, personnel, equipment).
The guidelines also state, "Blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, breathing pattern, heart rate, oxygen saturation, urine output and neurological status, among other parameters, should be monitored in a patient waiting for an ICU bed."
